What is Type 2-Diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition affecting millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the body either resists the effects of insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar, or doesn't produce enough insulin. This leads to high blood sugar levels, which can damage nerves and organs over time.
In this article, we will explore the symptoms and diagnosis of diabetes, as well as the causes and risk factors that contribute to its development. Whether you have been recently diagnosed with type 1 or 2 diabetes, or you are simply seeking to educate yourself about this prevalent disease, this article aims to provide you with valuable insights and information. So, let's embark on this journey together and learn more about type 2 diabetes, its symptoms, causes, and management strategies.
How Does Type 2 Diabetes Work?
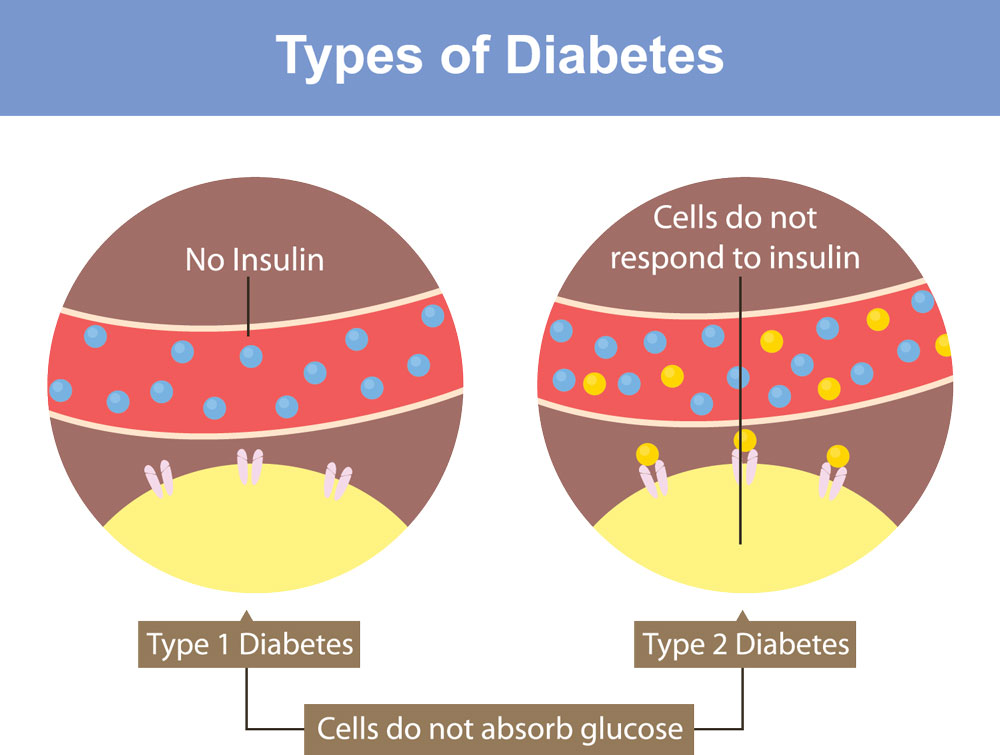
Difference between Type 1 and 2 Diabetes
Insulin acts like a key, unlocking cells to allow sugar (glucose) from your bloodstream to enter and be used for energy. In type 2 diabetes, either the cells become resistant to the "key" (insulin resistance) or the body doesn't produce enough "keys" (insulin deficiency). This leaves excess sugar circulating in the bloodstream, leading to various health problems.
Causes and Risk Factors.
Several factors increase the risk of developing diabetes, including:
- Genetics: Having a family history of diabetes raises your risk.
- Weight: Obesity and being overweight are significant risk factors.
- Physical Inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle increases risk.
- Diet: Consuming sugary drinks and processed foods can contribute.
- Age: The risk increases with age, though diabetes can occur at any age.
- Race/Ethnicity: Some ethnicities have a higher risk due to genetic predisposition.
- Socioeconomic Status: Limited access to healthy foods and healthcare can play a role.
Symptoms and Diagnosis.
Early stages of type 1 or 2 diabetes may not present any symptoms. However, common signs include:
- Increased thirst and urination.
- Excessive hunger.
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Fatigue.
- Blurred vision.
- Slow-healing wounds.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it's crucial to consult a doctor. A simple blood test can diagnose diabetes by measuring your blood sugar levels.
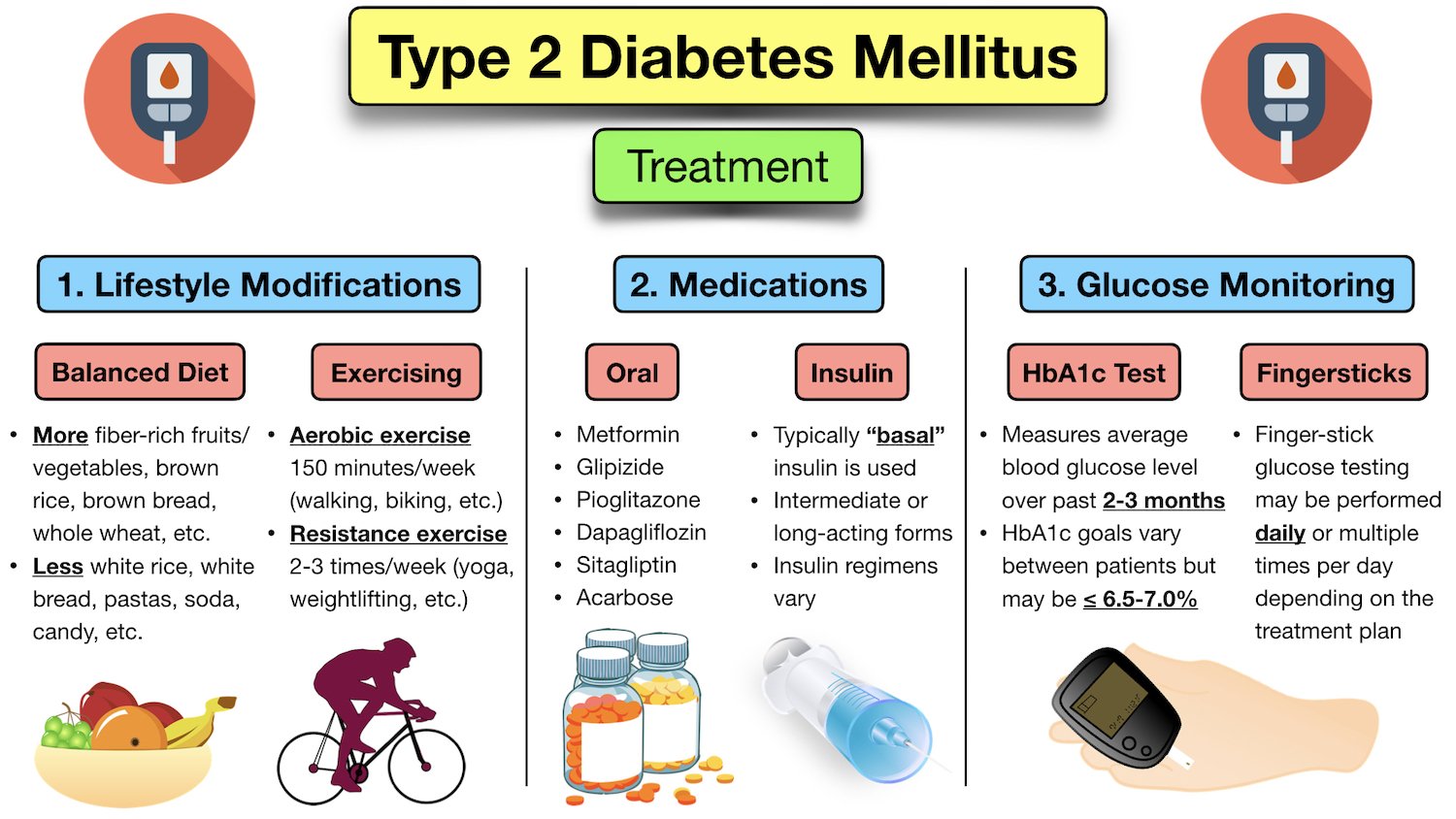
Treatment and Management

The cornerstone of managing diabetes involves lifestyle changes:
- Healthy Eating Opt for a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein.
- Regular Exercise Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Weight Management Losing weight, even a modest amount, can significantly improve blood sugar control.
In some cases, medication may be necessary to manage blood sugar levels. These include oral medications and injectable insulin. Emerging therapies like continuous glucose monitoring and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonists are also showing promise.
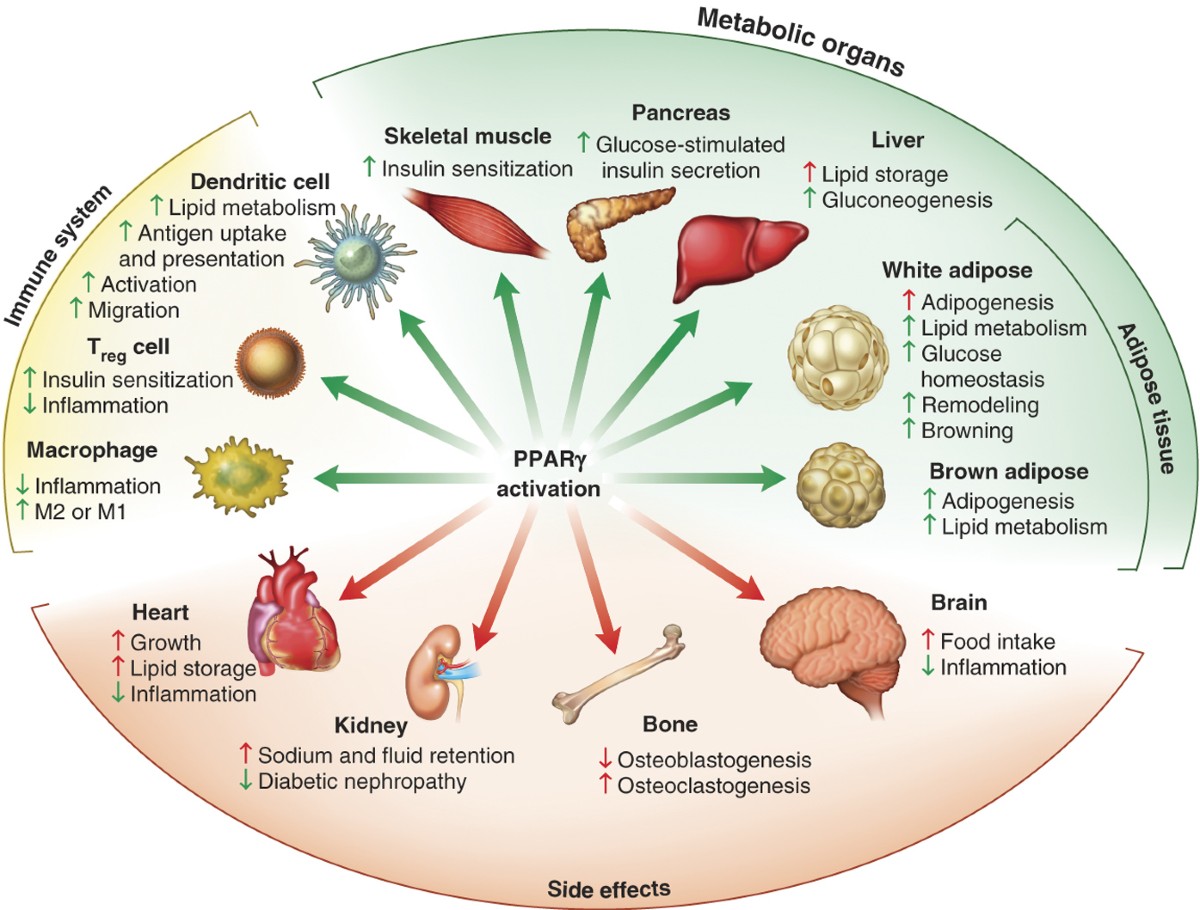
The Effects of PPARs on different areas of the human body
The Effects of PPARs on Type 2 Diabetes
PPARs (Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors) are a group of proteins that act like receptors in cells, regulating various functions, including blood sugar control. PPAR agonists are medications being investigated for their potential to improve insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) in metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Questions & Answers
Q: What are the main risk factors for developing type 2 diabetes, besides genetics?
Type 2 diabetes develops due to a combination of factors. Genetics play a role, but lifestyle choices significantly impact your risk. Obesity, physical inactivity, and a diet high in processed foods and sugary drinks are major contributors. Socioeconomic factors like limited access to healthy food and healthcare can also play a part.
Q: While type 2 diabetes is more common with age, why can it develop at any age, and what are some concerning trends related to this?
While age is a risk factor, type 2 diabetes can occur at any age, and it's becoming more prevalent in children due to rising childhood obesity rates. Typical symptoms include increased thirst and urination, fatigue, blurry vision, unexplained weight changes, and slow-healing wounds. However, some people may not experience any symptoms in the early stages.
Q:While lifestyle changes are a cornerstone of managing type 2 diabetes, what are some other treatment options that might be necessary in some cases?
The cornerstone of managing type 2 diabetes involves lifestyle modifications. Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein, combined with regular exercise, can significantly improve blood sugar control. Weight management is also crucial, as even modest weight loss can make a difference. In some cases, medication like oral medications or injectable insulin may be necessary to manage blood sugar levels.
Q: Research suggests a possible link between vitamin D deficiency and diabetes. Should I start taking vitamin D supplements to prevent diabetes?
A: While some research suggests a connection between low vitamin D levels and increased risk of type 2 diabetes, more evidence is needed to confirm a cause-and-effect relationship. It's important to consult your doctor before taking any supplements, including vitamin D. They can assess your individual needs and recommend the appropriate dosage, if necessary.
Q: I suffer from chronic hives. Could this be a sign of type 2 diabetes?
A: The connection between chronic hives and type 2 diabetes is relatively unclear. Chronic hives can have various causes, and diabetes is not a typical one. But through studies conducted, it is suggested that the lowering of glycemic levels via specific oral hyperglycemic medication would cause a sudden flare up of hives or rash. (Similar results can be observed from insulin injections sites in some patients, resulting in a rash or swelling around the injection site.)
It's best to consult a doctor for a proper diagnosis to determine the underlying cause of your hives. They can also screen you for type 2 diabetes if there are additional risk factors or concerning symptoms.
Metformin and the Risk of Chronic Urticaria in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Urticaria flare: an unusual factor limiting glycemic control
Q: I experience fatigue and swollen feet. Are these symptoms always indicative of type 2 diabetes?
A: Fatigue is a common symptom of type 2 diabetes, but it can also be caused by other factors like stress, lack of sleep, or certain medications. Swollen feet, however, could be a complication of uncontrolled diabetes. It's important to note that these symptoms alone don't necessarily mean you have type 2 diabetes. However, if you're concerned, it's crucial to consult a doctor for a proper diagnosis.
Diabetes symptoms: When diabetes symptoms are a concern
Why Diabetes Makes Your Feet Swell
Q: What are some promising new therapies being investigated for type 2 diabetes?
A: Researchers are continually exploring new treatment options for type 2 diabetes. One area of interest is PPAR agonists, medications that might improve insulin sensitivity in muscles of type 2 diabetic patients.
PPAR-gamma agonists and their role in type 2 diabetes mellitus management.
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) in metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes mellitus
PPAR-α and PPAR-γ agonists for type 2 diabetes
If you are curious on seeking other methods to treating and moderating diabetes, you can check out the following articles for new and upcoming therapies or medication being made available to the public.
Trailblazing Discoveries: The Top 5 Diabetes Research Breakthroughs of 2023
New and Emerging Drugs and Targets for Type 2 Diabetes: Reviewing the Evidence
But it is advisory for you to check in with your doctor to determine which is the best treatment for you.

